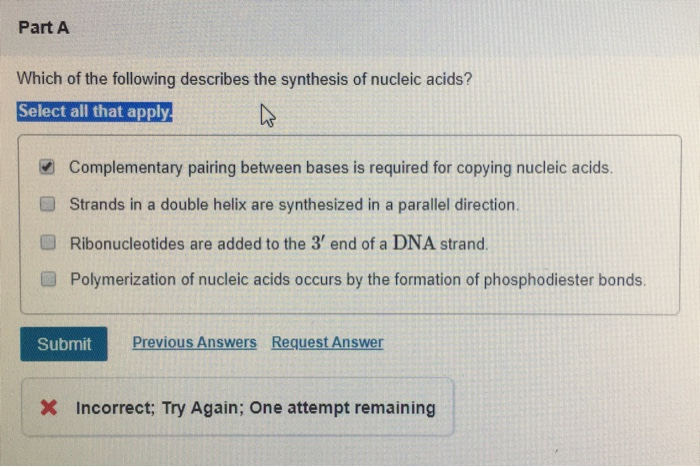
Complementary pairing between bases is required for copying nucleic acids. Up to 24 cash back Nucleic Acids Protein Synthesis 51.
Strands in a double helix are synthesized in an antiparallel orientation.
. Nucleic acid hybridization is a commonly employed procedure in molecular biology to investigate all EXCEPT. Provide an exact copy of the genetic code B. Deoxyribonucleotides are added to the 33 end of a DNADNA strand.
What type of change occurs to a nucleotide when it is activated. The main function of this process is to A. Which of the following best describes where mRNA processing is likely to occur.
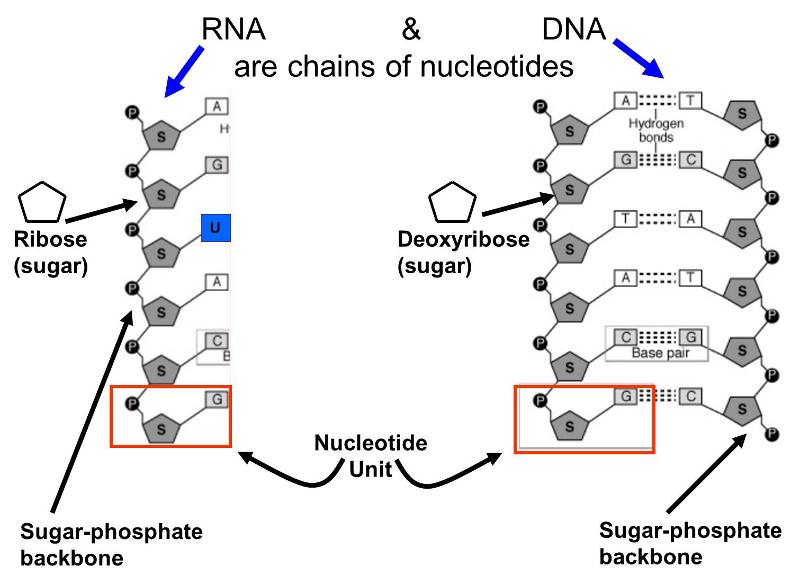
Nucleic acids including deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA store genetic information for living organisms. POLYMERS OF NON-REPEATING UNITS OF NUCLEOTIDES 7. Strands in a double helix are synthesized in a parallel direction.
Complementary pairing between bases is required for copying nucleic acids. Peptides form the backbone of a protein. Griffith called this process transformation DNA is made of four different types of nucleotides.
In some cells gene expression involves mRNA processing. THE FOLLOWING ARE DESCRIPTION OF NUCLEIC ACIDS. Ensure genetic variation in a species C.
Produce antibodies to combat disease Nucleic Acids. ALL OF THE FOLLOWING ARE TRUE ABOUT DNA EXCEPT. Nucleic acids are polymerized by the formation of peptide bonds between nitrogenous bases.
DNA is the chemical information system directing cell activities. Nucleotides link together to form a nucleic acid. Select all that apply.
Nucleus of prokaryotic cell B. Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA encodes the information cells need to make proteins. Information in mRNA is converted into a sequence of amino acids in a protein.
CONTAINS THE NITROGENOUS BASE. Synthesize cellular proteins D. Ribonucleotides are added to the 3 end of a.
Nucleic acids are polymerized by the formation of peptide bonds between nucleotides. A protein is held together by the carbon-carbon bonds. Complementary pairing between bases is required for copying nucleic acids.
Complementary pairing between bases is required for copying nucleic acids. Instructions from DNA in the nucleus are brought to the cytoplasm. Which of the following describes the synthesis of nucleic acids.
Therefore enzymes involved in these processes are attractive. What 3 major processes does DNA control. Amino acids link together to form a protein.
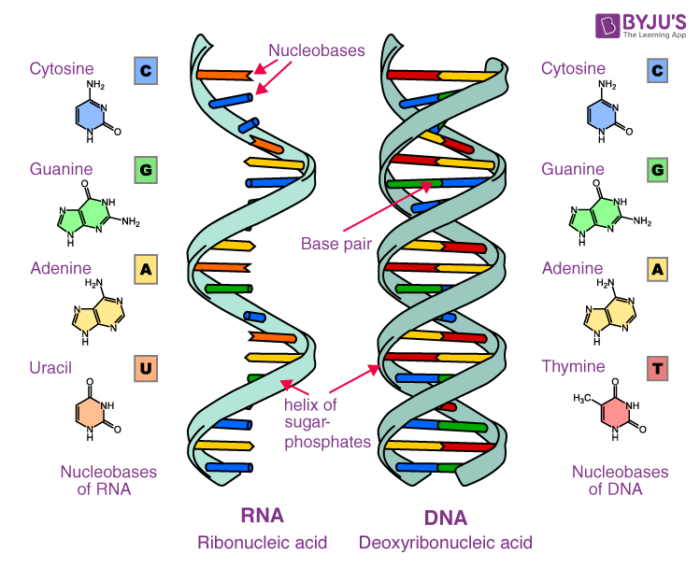
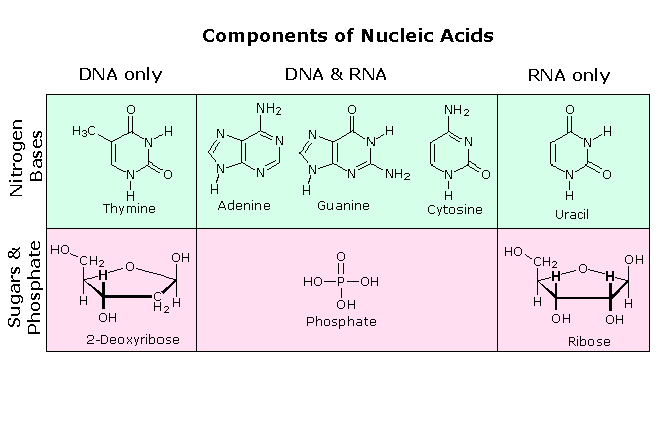
Nucleic acids are polymerized by the formation of peptide bonds between nucleotides. There are two types of nucleic acid and they are DNA and RNA. RNA is usually single-stranded and is made of ribonucleotides that are linked by phosphodiester bonds.
Ribosome of eukaryotic cell. A major function of nucleic acids involves the storage and expression of genomic information. Part A Which of the following describes the synthesis of nucleic acids.
Strands in a double helix are synthesized in a parallel direction such that one end of the molecule has two 3 ends and the other end has two 5 ends. A nucleic acid is held together by the sugar-phosphate complex. DNA is the basic guidelines for living things.
MADE UP ALSO OF A NUCLEOSIDE B. Which of the following describes the synthesis of nucleic acids. Strands in a double helix are synthesized in a parallel direction such that one end of the molecule has two 3 prime ends and other has two 5 prime ends.
Nucleic acids are polymerized by the formation of peptide bonds between nucleotides. A related type of nucleic acid called ribonucleic acid RNA comes in. COMPOSED OF CHAINS OF NUCLEOTIDES C.
What is Nucleic Acid Synthesis. Strands in a double helix are synthesized in a parallel direction such that one end of the molecule has two 3 ends and other has two 5 ends. Ribonucleic acid or RNA is mainly involved in the process of protein synthesis under the direction of DNA.
What functional groups define the two different ends of a strand. Use your textbook Chapters 13 14 and PP notes from lecture 1. A copy of chromosomal DNA is created.
Evolutionary relationships specific genes against a vast background specific probe based isolation of genes and quantify gene expression. Deoxyribonucleotides are added to the 33 end of a DNADNA strand. Nucleic Acids Protein Synthesis Name Complete the following worksheet over Nucleic Acid Structure DNARNA.
Complementary pairing between bases is required for copying nucleic acids. Cytoplasm of prokaryotic cell C. Complementary pairing between purines is required for copying nucleic acids.
Nucleic Acids Protein Synthesis 43. Nucleic Acids Protein Synthesis 42. A copy of chromosomal DNA is created.
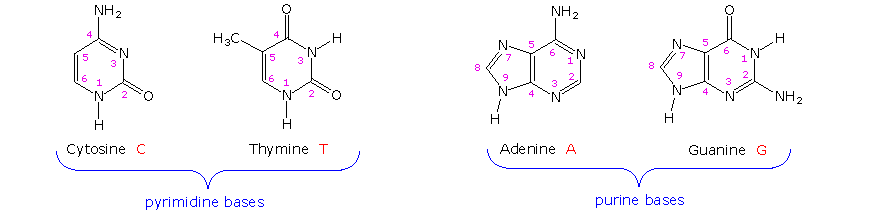
Nucleic Acids such as DNA and RNA are essential in genetics and are also useful in protein synthesis. The production and regulation of these biological macromolecules are essential for survival and replication of organisms. Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that play essential roles in all cells and viruses.
Complementary pairing between bases is required for copying nucleic acids Single strands of nucleic acids are directional meaning that there are two different ends. Nitrogen bases form the backbone of a nucleic acid. During his experiments to find a cure for pneumonia Frederick Griffith discovered that one strain of bacteria had been transformed into another.
Nucleic acids are essential because they secure up genetic knowledge in living things. 5 prime is phosphate and 3 prime is hydroxyl. The potential energy of the molecule increases.
VERY LARGE COMPLEX MOLECULES D. A RNA copy of a DNA strand is made. Question 2 30 seconds Q.
Nucleus of eukaryotic cell D. List several people that played a significant role in.
Solved Part A Which Of The Following Describes The Synthesis Chegg Com
What Is The Role Of Nucleic Acids In The Synthesis Of Proteins Neet
0 Comments